September 06, 2022
By: PhoenixBizz Staff Writer
PhoenixBizz is a division of Sofvue, LLC
Printed with permission of Data Titan and Sofvue LLC
The Internet of Things (IoT) technology is a network of devices that can communicate with one another through the Internet. IoT allows these devices to exchange data without human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction. IoT also allows businesses to collect information from these devices and analyze the data to improve business processes and make better decisions.
According to a report by McKinsey & Company, the Internet of Things (IoT) is poised to have an economic impact of $12.6 trillion by 2025. Another report by Statista indicates that the number of IoT devices will increase from 16.4 billion in 2022 to 30.9 billion by 2025.
These numbers indicate that IoT will greatly impact businesses in the coming years. So, for companies whose business can take advantage of Iot, there is no time like the present to develop solutions that can benefit their business.
Examples of transportation IoT include more efficient, less costly mass transit, which employ networks of sensors, digital cameras, and communication systems to increase system capacity and enhance passenger safety and comfort while lowering costs and risks.
This article covers key will discuss everything related to IoT, including what it is, its benefits for businesses, and how you can build an IoT app. Let’s get started!
What is IoT?
The best way to understand IoT is to first provide an actual, real-world example that solves an actual problem. So, consider traffic congestion… something we can all relate to. Using IoT technology, a municipality can set up digital cameras and sensor at different intersections and connect them via IoT so the sensors could “talk” to each other, providing real-time data about traffic congestion, but more importantly, when the sensors and cameras begin seeing congestion build up, can send real-time “rerouting” suggestions to a vehicles navigation system where an alternative route is available, thereby producing two positive outcomes, the first lessening the amount of traffic at an already congested intersection and second, helping the driver get to their destination more quickly. This is one example among a sea of million practical applications that IoT is just now beginning to tap.
The term "Internet of Things" (IoT) refers to a broad set of devices, vehicles, buildings, and other items—embedded with electronics, software, sensors, and connectivity that enable these objects to collect and exchange data.
IoT allows objects to be detected and/or controlled remotely across existing network infrastructure, creating opportunities for more direct integration of the physical world into computer-based systems.
What Are the Components of IoT?
The IoT ecosystem consists of sensors, actuators, gateways, cloud, and web-based and/or mobile apps for communications. The following are some definitions:
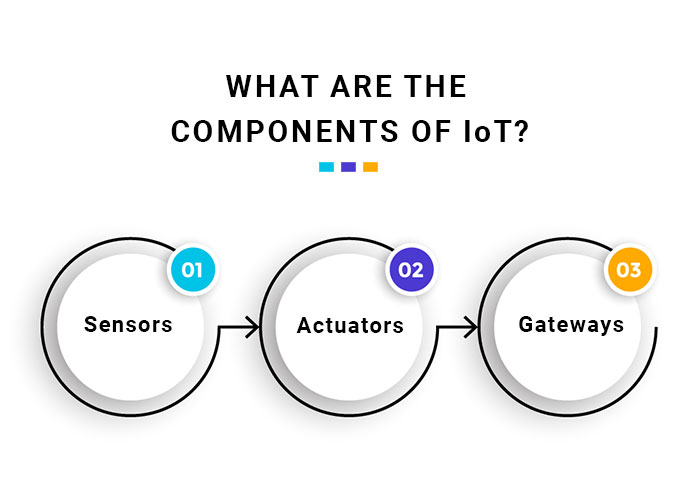
✅ Sensors: detect changes in the environment around them and send information about those changes over the internet so they can be analyzed by software running on another device.
✅ Actuators: enable a device to trigger an action in response to information collected by the sensor(s). Sometimes, this action might be like opening or closing a door or turning on lights when motion is detected in a room.
✅ Gateways: connect networks so that data can be sent between them seamlessly, even across networks running different protocols.
How Does IoT Work?
An IoT device is any object that can connect to the internet, communicate with other devices (also connected to the Internet), and then send data to another platform where it can be read and analyzed. As an example, retailers can use IoT technology to improve the customer experience by offering personalized shopping experiences, driven through their mobile device, based on their physical location in a store. Retailers can also use IoT for supply chain management, which includes managing their inventory levels or even issuing replacement orders directly from the company’s distribution center or from their preferred manufacturer locations.
What Does IoT Mean for eCommerce and Retail?
Including IoT in your company’s wheelhouse can great vast separation between you and your competitors. For example, the in-store experience can be enhanced so that a returning customer, when returning to their favorite store, can walk through the entrance and immediately be identified using sensors, RFID or digital cameras. Once identified, and while walking through the store, the customer might walk past an item that matches a similar item purchased during their last visit, and a notification could be sent to the consumers smart phone with a message stating there’s an item on the rack in front of them they might be interested in seeing.
This is what IoT means for ecommerce and retailers -- allowing customers to connect with your brand through their mobile devices, get new product recommendations, read reviews and compare prices easily (and quickly) from where they are standing.
Why Do You Need an IoT-Powered App?
You need customers interested in your products or services, so they'll buy from you—and the best way to do that is through an engaging mobile app that provides product offerings at the correct moment in time. IoT powered mobile apps provide more value for users than just being able to order goods online. They also provide easy access to product information like reviews, specifications, and discounts. You can also send your customers push notifications about sales and new releases and offer users access to exclusive content, whether they are in-store or standing in their kitchen preparing lunch.
Key Benefits of IoT App for Ecommerce Owners
Now that mobile technology is becoming mature (now 12 years since the first mobile apps began entering the marketplace), e-Commerce allows companies to understand their customers better, facilitate just-in-time inventory control and re-stocking, increase customer engagement, and improve inventory management.
#1 Increase Customer Engagement
IoT is an exciting technology that allows retailers to engage with their customers frequently, and with viable content, improving the shopping experience, generating higher cart values and promoting brand loyalty.
Examples of how physical storefronts can utilize e-Commerce IoT include:
✅ Adding product recommendations based on customers' demographics, location, and previous purchases.
✅ Sending push notifications when a product goes on sale or when it's first available for purchase (e.g., if you're interested in a pair of shoes, receive an alert as soon as they are released).
✅ Offering rewards programs through unique codes printed on receipts or packaging that can be redeemed online or offline for discounts at other locations at the same chain (i.e., if you spend $200 this week, get 10% off your next purchase).
#2 Bring Customers Back with Push Notifications
Another tactic that can serve your business well is push notifications. These are the notifications sent directly to a user’s phone and can be customized to target your audiences better.
Push notifications sent to a customer’s home screen (on their phone) remind customers of new products you offer, upcoming sales or events, reminders about your store location and hours, and more. You can also send targeted push notifications based on a customer's actions within an app, such as when they add an item to their shopping cart but fail to complete the in-app purchase.
#3 Improving Inventory Management
Inventory control is the backbone of every retailer. Get this wrong and you are out of business, so it's important to have real-time inventory depletion management controls to ensure you are either (a) always stocked and/or (b) ensure that items become unavailable when reaching minimum floor counts (including active items already in shopping carts) awaiting purchase. The good news is that IoT can help.
Using smart sensors and other data-gathering tools, retailers can keep track of their inventory in real-time. Using these sensors, warehouses and inventory rooms can monitor critical information about products, including its availability, expiration date, and do so without any human control.
#4 Better Supply Chain Management
With IoT devices, you can track an item's journey precisely. IoT sensors combined with RFID (Radio Frequency Identification Tags) help businesses stay current with what is happening with the product, including its location, time to arrival, condition, and more. This helps you predict arrival times and avert losses or wrong delivery locations.
One of the biggest examples is Amazon’s IoT-powered robots which manage the selection, placement, packaging, and other necessary tasks to ship orders quickly. These robots might not do all the work in the distribution center, but they can certainly do the majority.
Steps to Developing an IoT-based Ecommerce App
Interaction with IoT devices has become one of the keys to e-Commerce success. With the growing popularity of smart homes, self-driving cars, and wearable technology, consumers will increasingly assume and expect that the commerce they conduct with retailers will automatically include many of the features we’ve discussed.
As a small business owner, consider these points.

Step#1 Define Your Requirements
The first step to developing a viable e-Commerce mobile app is defining all your business requirements. The requirements gathering process is sometimes time-consuming and laborious, but the process is worth its weight in gold at the end. To this end, your requirements should answer the following questions:
◾What are the business goals? Why do you need this app? How does it help your company or customers?
◾How will ROI be defined for the project? For some projects, ROI is measured through increased sales or revenue growth, while in other projects, ROI is more abstract and focuses on time saved, productivity gains and even employee or customer satisfaction.
◾What data do you need, and how much of that data can be stored locally on devices instead of cloud-based servers (or vice versa)?
◾Who are the users? What are the users' needs for offline and online mode operation, and how often should they be refreshed by updating apps from an app store (or other sources)? How big should these updates be so they don't take up too much space on users’ mobile devices?
◾Are there any technical requirements such as device capabilities like GPS tracking; cell-tower triangulation, high-resolution screens; NFC/RFID/BLE connectivity etc., which might require additional hardware features like cameras or microphones being present in devices?
Additionally, you should consider how your customers will interact with their products and services through a mobile app, and additionally, how much backward compatibility is too much, and which platforms must the app support. The next thing you have to consider is cost, which can be broken down into two parts:
✅ Hardware costs (such as sensors, camera’s, etc.)
✅ Software development costs (which vary based on whether you build from scratch or use an existing platform)
Step#2 Consider the User Experience (UX)
User experience (UX) is the sum of all user interactions with your application services and/or mobile app. These may be in person, on the web, via mobile app, or through voice interaction.
The User Journey will make or break your business model. If users find your app challenging to use, they will churn never to return.
To ensure that the user experience for users is nothing short of perfect, make sure:
✅ The mobile app’s UX is simple, intuitive, and easy to use so that anyone can use it with limited training.
✅ The user experience across all devices, platforms, and operating systems (OS) is agnostic, meaning that no matter what device or OS your customer uses, the same look and feel will exist across all screens.
Step#3 Create a Prototype
If you're in the initial stages of development and are still trying to understand how your app would work, it is crucial to create a prototype.
A prototype is essentially a working model of your concept. It can be used for testing purposes—such as testing the user interface or key features. In fact, there are many reasons why prototyping is essential:
✅ You can use prototypes as part of usability studies to test ideas and get feedback from potential users about what they want to see in an app.
✅ You can also use prototypes during meetings with investors or potential partners so that everyone on the team knows what the final product will look like before creating it entirely from scratch.
A prototype doesn't have to be fancy; many people choose simple designs that look similar to what they want their apps' interfaces (or even websites) to eventually look like when completed.
Step#4 Build Your App
The next step is to either decide to build the app yourself or identify the right company who can build your app. If you have deep knowledge of Xcode, Java or one of many third-party cross platform development tools, you’re set. If not, you’ll need to contract with an eCommerce app development company with the right experience in IoT app development.
When it is the latter, do the following:
✅ Ask them to provide proof of other completed mobile app projects in the past year
✅ Ask them to provide you with at least a dozen letter’s of recommendations
✅ Ask them to define what approach they take in developing e-Commerce mobile apps, with and/or without Iot
This will help you make an informed decision and prevent the many pitfalls that can surface during development cycles.
Step#5 Test and Deployment
The next step is to validate all the functionality associated with the mobile app. Often times, people assume, wrongly, that QA and testing represents less than 10% of a project, and although this is true in some projects, most often, it’s not true, and the project’s testing can absorb 30% or even 40% of the overall developments lifecycle. As a result, you will need a very experienced team who can execute the QA and UAT that comes with many projects.
Once testing is complete comes deployment. During the pandemic, deployment times for Apple Store mobile apps were taking 10-20 days for approval, and in one project, over 30 days. For Google Play Store, they were taking about 10 days. As of this articles release date (September of 2022), approval times have vastly improved with most of our projects being approved in 3-5 business days, on both the Google Play Store and the Apple Store.
Final Thoughts
The Internet of Things (IoT) is growing rapidly, and to remain competitive, you have to use the latest tools and technology to out-perform your competitors. By using IoT-powered applications, you can attract and retain more customers, create value-added services to your business’ bottom line and ultimately, over time, significantly improve your company’s ROI.
Ready to take advantage of IoT in today’s marketplace? PhoenixBizz has been designing and developing mobile and web-based application systems since 2004. We’ve began developing mobile app solutions in 2009, just two short years after the launch of the Apple Store, then in 2012 for the Google Play Store, and to date, we have designed and developed over $22MM in solutions for companies coast-to-coast, and across numerous business segments. Give us a call to learn more about our recently completed projects and to discuss how we can serve your company.
Read this blog: Why Internet Of Things (IoT) Is An Emerging Buzzword In Today’s Technology?